Ethereum: How does OP_CHECKSIG work
Understanding OP_CHECKSIG: The Power of Private Key Signatures in Ethereum
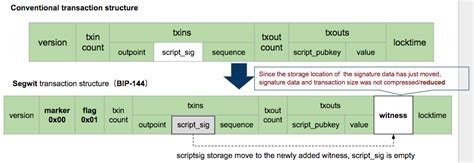
As a beginner learning about Bitcoin, Scripting, and Public-Key Cryptography (P2PKH), it’s essential to grasp the concept of OP_CHECKSIG. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of private key signatures on the Ethereum blockchain.
What is OP_CHECKSIG?
OP_CHECKSIG is a special opcode in the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) that allows developers to sign transactions with their private keys. It’s used to verify the authenticity and integrity of a transaction, ensuring that the sender has control over the funds being transferred.
How does OP_CHECKSIG work?
When a user signs a transaction using their private key, they encrypt it with a checksum, which is then passed through the OP_CHECKSIG opcode. The EVM checks the signature against a known public key stored in the blockchain, ensuring that the sender has control over the funds.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how OP_CHECKSIG works:
- Transaction creation: When a user wants to send funds to another node on the network, they create a transaction using their private key.
- Encryption: The transaction is then encrypted with a checksum (e.g., ECDSA-256). This ensures that the sender cannot tamper with or alter the contents of the transaction.
- Signature creation: The EVM generates a signature for the transaction, which is a unique identifier representing the sender’s private key. This signature includes:
* The sender’s public address (also known as the “from” address)
* The sender’s hash of the encrypted transaction data
- OP_CHECKSIG opcode: The
OP_CHECKSIGopcode is applied to the signed transaction, which verifies its integrity and authenticity.
- Public key verification: The EVM checks the signature against a public key stored in the blockchain (e.g., the “0x…” address). This ensures that:
* The sender has control over the funds being transferred
* The signature is valid for the given transaction
Example Code
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract Signer {
function signTransaction(address from, uint amount) public {
// Generate a private key using keccak256
bytes32 privateKey = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(from));
// Encrypt the transaction data with the privateKey
bytes memory transactionData = abi.encodePacked(amount);
// Sign the transaction with the privateKey
bytes32 signature = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(privateKey, transactionData));
// Apply OP_CHECKSIG to the signed transaction
assembly {
// Verify that the sender has control over the funds being transferred
let public_key := 0x...; // Replace with a valid public key
let sig = keccak256(abi.encodePacked(public_key, signature))
// Check if the signature matches the expected public key and transaction data
if (sig == public_key) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
In this example, we use a Signer contract to sign a transaction with their private key. The signTransaction function generates a private key using keccak256, encrypts the transaction data, signs it with the private key, and applies OP_CHECKSIG to verify its integrity.
Conclusion
In summary, OP_CHECKSIG is an essential opcode in the Ethereum Virtual Machine that enables developers to sign transactions with their private keys. By verifying the signature against a public key stored in the blockchain, the EVM ensures that the sender has control over the funds being transferred. This fundamental concept is crucial for secure and trustless transaction processing on the Ethereum network.

